Featured
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
CHARACTERISTICS OF DNA
CHARACTERISTICS OF DNA
Introduction:-
DNA, or Deoxyribonucleic acid, is a complex molecule that contains the genetic information necessary for the development and function of all living organisms. The structure of DNA was first discovered in 1953 by James Watson and Francis Crick, and it has since been the subject of extensive study and research. In this blog, we will discuss the characteristics of DNA and how they contribute to its role in life.
Double Helix Structure:-
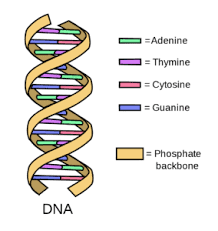
The most well-known characteristic of DNA is its double helix structure, which consists of two long strands of nucleotides twisted around each other. The nucleotides in DNA consist of four nitrogenous bases – adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine – which are paired in a specific way. Adenine always pairs with thymine, and guanine always pairs with cytosine. This base pairing ensures the fidelity of DNA replication and transcription, as the complementary bases can only form specific hydrogen bonds with each other.
Semi-conservative Replication:
Another key characteristic of DNA is its ability to replicate itself in a semi-conservative manner. During replication, the helix are separated, and each strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand. As a result, each new DNA molecule contains one strand from the original molecule and one new strand. This semi-conservative replication ensures that genetic information is passed on from parent to offspring with a high degree of accuracy and fidelity.
Genetic Information:
DNA is the carrier of genetic information, which is stored in the sequence of the nucleotides. The sequence of bases along the DNA molecule forms a code that determines the genetic traits of an organism. The genetic code is read in groups of three bases, called codons, which correspond to specific amino acids. The sequence of amino acids determines the structure and function of proteins, which are essential for the function of cells and the organism as a whole.
Mutations:
While the fidelity of DNA replication is high, errors can occur, leading to mutations in the genetic code. Mutations can be caused by external factors such as radiation or chemicals, or they can occur spontaneously during replication. Mutations can have a range of effects on an organism, from no effect to severe consequences such as genetic disorders or cancer. Some mutations can even be beneficial and lead to evolutionary changes.
Non-coding Regions:
While much of the focus on DNA has been on the genetic code, it is important to note that not all DNA codes for proteins. In fact, only a small percentage of the DNA in an organism’sEpigenetics:
In addition to the genetic code, the way that genes are expressed can also be influenced by epigenetic modifications to the DNA molecule. These modifications can include methylation, histone modification, and chromatin remodeling, among others. Epigenetic modifications can affect gene expression without changing the underlying genetic code, and can be passed on to future generations.
DNA Packaging:
Because DNA is a long, thin molecule, it needs to be packaged into a compact structure to fit inside the cell. In eukaryotic cells, DNA is packaged into chromosomes, which consist of DNA wrapped around proteins called histones. This packaging helps regulate gene expression and ensures that the genetic information is passed on accurately during cell division.
Repetitive DNA:
Another characteristic of DNA is the presence of repetitive DNA sequences, which can make up a significant portion of an organism’s genome. These sequences can be repeated thousands or even millions of times, and may serve as structural elements, help regulate gene expression, or have other functions.
DNA Repair:
Because DNA is constantly exposed to damage from external and internal factors, cells have evolved mechanisms to repair damaged DNA. These repair mechanisms can fix many types of damage, including breaks, chemical modifications, and base mismatches. Failure of these repair mechanisms can lead to mutations and genetic disorders.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, DNA is a complex molecule with a range of characteristics that contribute to its role in life. Its double helix structure, semi-conservative replication, and genetic code are essential for passing on genetic information from one generation to the next. Mutations and non-coding regions also play important roles in shaping the genetic makeup of organisms. Understanding the characteristics of DNA is essential for understanding the biology of life and the mechanisms of evolutioni. Overall, the characteristics of DNA are essential for its role in life, from passing on genetic information to regulating gene expression and maintaining genome stability. Understanding the complexity of DNA is a key area of study in biology and has broad implications for fields such as medicine, biotechnology, and genetics.
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Popular Posts
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment